Material in this article is adapted from:
For additional information:
The brain is the control center of the body and mind, governing everything from movement, sensation and speech, to thought, emotion and memory. Because the brain is divided into regions that control specific functions throughout the body, a tumor in a particular area of the brain is likely to have an impact on the actions it governs.

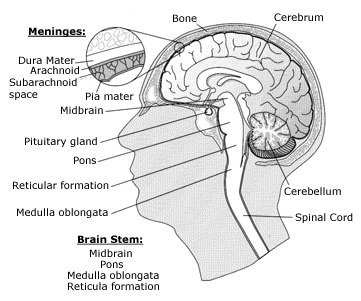
The brainstem controls our most basic functions, many of which happen without our thinking about them at all. Three structures make up the brainstem:
Every year, about 2,000 American children under the age of sixteen are diagnosed with a brain tumor. There are many different types of brain tumors. Brain tumors can vary in how they grow, affect the body, and respond to treatment.
A tumor is any abnormal mass in or on the body that is caused by an accumulation of cells dividing--and thus increasing in number--in an uncontrolled way. Primary tumors are made up of cells unique to the organ or tissue where they start. Secondary tumors start somewhere else in the body and spread, or metastasize, to one or more sites.
Most brain tumors in children are primary, meaning that they start in the brain and are not the result of malignant cells spreading to the brain from another location in the body. A primary tumor in the brain rarely spreads beyond the brain and spinal cord.
The cause of most brain tumors is not known. Researchers are looking into environmental and genetic factors for clues, but there are little conclusive data on what causes childhood tumors that start in the brain.
In most cases- no. A tumor is termed cancerous because of the way the cells appear under the microscope and it's ability to spread, or metastasize, beyond it's original site to other parts of the body. Many primary brain tumors are benign pathologically but are considered "malignant" due to their location within the brain. Thus, psychologically and practically, brain tumors are a lot like cancerous tumors. The treatments are often the same, and resources that are helpful to cancer patients, such as cancer support groups, the American Cancer Society, and the National Cancer Institute, are helpful to patients with brain tumors.
Faith had a brainstem glioma, specifically a diffuse pontine glioma.
Brain and spinal tumours in childhood (0-15 years) account for 20-25% of childhood cancer, affecting one in 2500 children. Within the group of brain and spinal tumours there are a number of well defined categories with characteristic clinical presentations, biological behaviour, and suitability for specific treatment approaches. These factors combine to predict a range of outcomes from the highly curable tumours (> 80% 10 year survival rate) such as germinoma and cerebellar astrocytoma, through to the virtually incurable brainstem glioma. Brainstem gliomas account for about 10% of all brain and spinal tumours.
We define the brainstem as extending from the midbrain (tectal plate) to the medullary cervical junction . Therefore, brainstem glioma is a term describing a collection of anatomically related tumours with characteristic appearances on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Because they are frequently not biopsied, "glioma" is used as a "catch all" term unless a histological diagnosis has been made.
Most brainstem gliomas transiently respond to radiotherapy as judged by the alleviation of neurological symptoms and evidence for improved duration of survival in patients given higher doses (> 50 Gy v < 50 Gy) of radiotherapy For those with diffuse characteristics located within the pons, the duration of response is brief and progressive symptoms can be expected at a median of about nine months after diagnosis.
Because of their location, brainstem gliomas typically cause sudden dramatic symptoms, such as double vision, clumsiness, difficulty swallowing and weakness. Surgery is not usually an option. Radiation therapy, with or without chemotherapy is preferred.